The adoption of 5G technology revolutionises mobile users’ experience with cutting-edge technical capabilities for high speed, high capacity, high reliability, massive connectivity and low latency communications. 5G opens up vast potential for various commercial and smart city applications such as smart surveillance, time-critical remote operation, telemedicine and intelligent transportation.

In 2019, the CA assigned a total of 1 980 MHz of radio spectrum in the 3.3 GHz, 3.5 GHz, 4.9 GHz, and 26 GHz and 28 GHz bands in a timely manner for public mobile telecommunications use, including the provision of 5G services. MNOs launched their commercial 5G services in Hong Kong starting from 1 April 2020. As of March 2022, 5G coverage in Hong Kong had reached over 90% and even up to 99% in core business districts, covering major locations in the urban areas and all MTR lines.
In order to meet the growing needs of various 5G applications in terms of speed, capacity and coverage, OFCA supported the CA to release more spectrum in different frequency bands to the market. Following the promulgation of the decisions of the CA and SCED by way of joint statements on 30 March 2021 on the arrangements for frequency allocation and assignment of additional spectrum for 5G services, and the related spectrum utilisation fee (SUF), OFCA conducted a spectrum auction in October 2021 and assisted the CA in assigning 80 MHz of spectrum in the 4.9 GHz band in December 2021, and 70 MHz of spectrum in the 700 MHz band in June 2022 according to the auction results.

Three incumbent MNOs were each assigned 400 MHz of spectrum in the 26 GHz and 28 GHz bands for the provision of large scale public mobile services in April 2019. They were each under a network and service obligation to install and put into use a total of 2 500 radio units in three phases, by April 2022, April 2023 and April 2024 respectively. In April 2021, the three MNOs made a joint request to the CA on postponement to fulfil the network and service rollout milestones by two years, due to the later-than-expected availability of the relevant network equipment and handsets supporting the 26 GHz and 28 GHz bands. Taking into account the MNOs’ submission and OFCA’s assessment, the CA decided in November 2021 to amend the network and service rollout obligations imposed on them by postponing each of the three network and service rollout milestones by two years from 2022–24 to 2024–26. Notwithstanding the postponement of the milestones, the total minimum number of 2 500 radio units required to be installed and put into use remains unchanged.
OFCA implemented the “Subsidy Scheme for Encouraging Early Deployment of 5G” launched by the Government under the Anti-epidemic Fund in May 2020. The scheme aims to encourage early deployment of 5G technology across trades and industries for improving efficiency, productivity and quality of service. Under the scheme, each approved project will be subsidised for 50% of the actual cost directly relevant to the deployment of 5G technology, subject to a cap of HK$500,000. The total amount of funding earmarked for the scheme is HK$100 million.
Since its launch, the scheme has been well received with enthusiastic responses. As of 31 August 2022, a total of 152 applications had been approved, covering various sectors including construction, design, education, environmental protection, e-sports and recreation, event and exhibition, finance, logistics, medical and healthcare, property and building facilities management, repair and maintenance, sales and marketing, telecommunications, textiles, and transport.
To further encourage the public and private sectors to deploy 5G technology and foster innovation, the Government has extended the deadline for application to 31 December 2022. OFCA will continue to provide support for operation of the scheme.
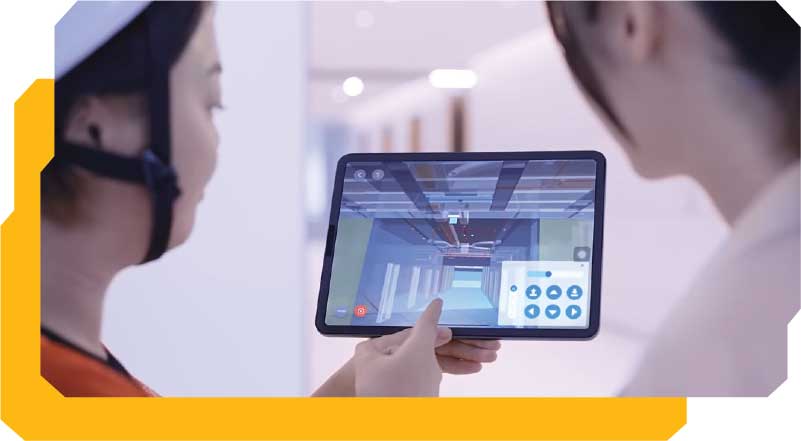

5G technology can also apply to construction, property and building facilities management which helps enhance efficiency and quality of service.
In support of the Government’s policy initiative, OFCA is implementing a subsidy scheme with a funding of HK$770 million to provide financial incentives for FNOs to extend their fibre-based networks to 235 villages across nine districts in the New Territories and outlying islands. These villages are located far away from the existing fibre-based backbone networks of FNOs, where villagers can only choose broadband services delivered over copper-based networks at a speed of 10 Mbps or below.
The 235 villages are grouped under six projects (namely, Project 1 to Project 6) for tendering purpose. Selected FNOs are required to roll out fibre-based lead-in connections to the vicinity of the entrances of the villages concerned, and roll out three submarine fibre-based cables connecting Lamma Island from Hong Kong Island (under Project 5), as well as connecting Cheung Chau from Lantau Island and Peng Chau from Lantau Island (under Project 6). To introduce competition, selected FNOs are required to open up at least half of the capacity of the network facilities and submarine fibre-based cables subsidised under the scheme for use by other FNOs for free.
Following the award of all six tender projects under the scheme between November 2019 and May 2020, the selected FNOs have already extended their fibre-based networks to 67 villages as of 31 August 2022. It is expected that fibre-based networks will connect to all the villages covered by the subsidy scheme by 2026.
With the extension of the fibre-based networks, not only will the villagers concerned be able to enjoy high-speed fixed broadband services, MNOs will also be able to make use of the new networks as backhaul for their mobile networks and provide high-speed and innovative mobile services including 5G services to the areas concerned.
For the deployment of 5G services in Hong Kong, MNOs are required to establish a larger number of radio base stations (RBSs) as compared with previous generations of mobile services. To facilitate the expedient and effective rollout of 5G networks, OFCA launched a pilot scheme in March 2019 to open up more than 1 000 suitable government premises for MNOs to install RBSs with a streamlined approval process and nominal rental (HK$1 per year). OFCA has set up a dedicated team to coordinate with MNOs and relevant government departments on the matters concerned, and issued the “Guidance Notes for Submission of Applications under the Pilot Scheme for Installation of Radio Base Stations at Selected Government Venues” to set out the principles, requirements and streamlined procedures in respect of the applications under the scheme. In January 2022, OFCA launched the second phase of the Pilot Scheme by further opening up about 500 government premises under a “demand-led” model for MNOs to install RBSs. As of August 2022, 168 applications had been received under the scheme, of which 101 were approved.
OFCA has also been coordinating with the relevant government departments to facilitate MNOs’ access to suitable street furniture and public facilities such as public payphone kiosks and sheltered bus stops for the installation of RBSs. We issued the “Guidelines on the Use of Public Payphone Kiosks for the Installation of Radio Base Stations for Provision of Public Mobile Services” and the “Guidelines on the Use of Sheltered Bus Stops for the Installation of Radio Base Stations for Provision of Public Mobile Services” in April and November 2020 respectively to facilitate the industry’s use of the public payphone kiosks and sheltered bus stops for installation of RBSs. OFCA will continue to work with the industry and the relevant government departments in identifying other suitable street furniture and public facilities for installation of RBSs and facilitating technical trials.
Since the 3.4–3.6 GHz (3.5 GHz) band has been reallocated from fixed satellite service to mobile service with effect from 1 April 2020, OFCA supported the CA to delineate two restriction zones in Tai Po and Stanley to enable the coexistence of the existing earth stations for telemetry, tracking and control of the licensed satellites in orbit (TT&C stations) and systems of public mobile services operating in the same and adjacent bands. In response to the industry request and with input from the stakeholders, OFCA further supported the CA to issue the guidelines entitled “Guidelines for Installation of Radio Base Stations Operating in the 3.4–3.6 GHz Band within the Restriction Zones Delineated by the Communications Authority” in July 2019 such that MNOs can deploy 3.5 GHz RBSs within the restriction zones in a controlled manner.
To fully resolve the issue of the “3.5 GHz restriction zone” in Tai Po, OFCA has proactively liaised with the concerned satellite operators regarding the relocation of their TT&C stations operating at the 3.5 GHz band from Tai Po to the Chung Hom Kok Teleport, so that MNOs can make wider use of all the available 5G bands (including the 3.5 GHz band) in Hong Kong for the provision of 5G services. With OFCA’s assistance, one of the satellite operators has been granted a land lot for relocation of its TT&C stations from Tai Po to the Chung Hom Kok Teleport, while the other operator has undertaken to install satellite band-pass filters at their satellite facilities to prevent radio interference.
Relocation of the TT&C stations involves complex land and technical issues, including site selection, land grants, site formation, construction works and establishment of another set of satellite antennae as well as the need to ensure that operation of the existing satellites in orbit will not be affected. Considering the lead time and effort required for completing the relocation exercise, it is expected that the “3.5 GHz restriction zone” in Tai Po can be removed before the end of 2024. In the meantime, MNOs are making use of other 5G bands (e.g. the 4.9 GHz band) or have re-farmed their existing spectrum (e.g. the 2.1 GHz band) to provide 5G services in the “3.5 GHz restriction zones” in Tai Po.
Since the creation of a new licensing regime by the CA in December 2017 for the provision of Wireless Internet of Things (WIoT) platforms and services using the shared frequency band of 920–925 MHz, three WIoT licences have been issued. In addition, the existing MNOs may also make use of the frequency spectrum assigned to them under the Unified Carrier Licence to provide WIoT services by adopting mobile technologies such as Narrowband Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G technologies that enable massive IoT connections. OFCA will continue to support the CA to facilitate the development and competitive supply of WIoT services in Hong Kong.

The Localised Wireless Broadband Service Licence (LWBS Licence) was created in July 2019 to enable the use of 400 MHz of spectrum in the frequency range of 27.95–28.35 GHz on a geographically shared basis (Shared Spectrum) for the provision of innovative wireless broadband services. The first LWBS Licence was issued to the Airport Authority in October 2019 for implementation of smart airport initiatives.
In order to facilitate the use of the Shared Spectrum for the establishment of 5G systems for private use by different entities in the community, OFCA supported the CA to create the Localised Wireless Broadband System (Private) Licence (LWBS (Private) Licence) in December 2021. The LWBS (Private) Licence is subject to a more light-handed regulation and lower level of licence fee compared with LWBS Licence, given that its scope of operation is limited to private use and is of a smaller scale.
OFCA will process new applications for LWBS Licence and LWBS (Private) Licence with a view to facilitating the development of innovative 5G and smart city applications at different locations, such as university campuses, industrial estates and technology parks.
The CA announces the creation of a new Localised Wireless Broadband System (Private) Licence.
On 30 September 2021, a new 15-year term of assignment commenced for 150 MHz of spectrum in the 1800 MHz band upon expiry of the previous term. As some of the spectrum in the 1800 MHz band would change hands upon re-assignment, OFCA convened a technical working group as early as in May 2019 comprising representatives of all four MNOs to coordinate the relevant technical arrangements to reconfigure their existing networks and/or roll out additional network infrastructures. Through the efforts of the technical working group, the spectrum in the 1800 MHz band was smoothly handed over to the new assignees on 30 September 2021.
The current assignment of 90 MHz of spectrum in the 2.5/2.6 GHz band will expire in March 2024. Separately, 15 MHz of spectrum in the 850 MHz band, with the previous assignment originally due to expire in November 2023, was returned by the spectrum assignee in June 2021 upon approval granted by the CA. Following the issue of the joint statements by the CA and SCED on 30 March 2021 announcing the arrangements for re-assignment of the spectrum in the 850 MHz and 2.5/2.6 GHz bands and the related SUF upon expiry of the existing assignments, OFCA assisted the CA in implementing the decisions to re-assign 105 MHz of spectrum in the 850 MHz and 2.5/2.6 GHz bands, together with assignment of 150 MHz of new spectrum in the 700 MHz and 4.9 GHz bands, by way of a single auction held and concluded in October 2021. Pursuant to the auction results, 15 MHz of spectrum in the 850 MHz band was re-assigned in December 2021, while 90 MHz of spectrum in the 2.5/2.6 GHz band will be re-assigned upon the expiry of the existing assignments in March 2024.
OFCA keeps up with worldwide development trends in telecommunications and participates in related international/regional meetings of the International Telecommunication Union and Asia-Pacific Telecommunity, among others. Through various formal and informal channels, OFCA has been maintaining dialogue with the industry players in Hong Kong to keep abreast of the development of the telecommunications industry. An in-house task force on spectrum supply has been set up in OFCA to collate efforts with a view to conducting early spectrum planning work and ensuring timely release of suitable spectrum to meet the demands of emerging new radiocommunications services and facilitate the ongoing development of public mobile (including 5G) services. Taking into account OFCA's recommendations, the CA issued the Spectrum Release Plan for 2022–2024 in February 2022 to inform the industry of the potential supply of spectrum for provision of public mobile and/or other radiocommunications services in the coming three years.
With OFCA’s support, the CEDB completed the review of the telecommunications regulatory framework under the TO. The Telecommunications (Amendment) Ordinance 2021 (Amendment Ordinance) came into operation on 24 June 2022 and amended relevant provisions of the TO to implement four major measures proposed in the above review, namely stipulating the powers of the CA on regulating the telecommunications functions of smart devices, strengthening the protection of underground telecommunications infrastructure, simplifying the licensing framework to facilitate the introduction of innovative services and improving the appeal mechanism under the TO.
Under the new section 18A of the TO, it is a criminal offence for any person not to take reasonable steps to protect or fails to prevent damage to an underground telecommunications line when carrying out any work below ground level near the line. In this regard, OFCA assisted the CA to issue the “Guidelines on Work near Underground Telecommunications Lines” on 25 February 2022 (the Guidelines) to provide relevant stakeholders with practical guidance for compliance with section 18A. According to the Guidelines, the working party shall appoint a competent person to carry out the detection work for the underground telecommunications lines. In this connection, OFCA has liaised with two training course providers, namely the Hong Kong Institute of Construction and the Hong Kong Institute of Vocational Education, to offer relevant training courses since March 2022. Applicants who have completed the training and met the relevant qualification requirements may apply to OFCA to become competent persons. The list of competent persons is published on OFCA's website.

Pursuant to the Amendment Ordinance, the Telecommunications Appeal Board (TAB) is formally set up to replace the previous Telecommunications (Competition Provisions) Appeal Board. In addition to dealing with decisions of the CA in relation to exploitative conduct engaged by licensees under section 7Q of the TO, the TAB will also handle certain decisions of the CA under the TO.
The Government engaged the four local MNOs to set up an emergency alert system (EAS), enabling the Government to send time-critical messages via the MNOs’ mobile networks to alert the public to take contingency measures as soon as possible during emergency situations, such as unforeseen extreme weather conditions. On 9 March 2022, the Government used the EAS for the first time to disseminate an emergency message to the public. OFCA will continue to monitor MNOs’ operation and maintenance of the EAS, and assist different bureaux/departments in disseminating emergency messages via the EAS as necessary.
The Telecommunications (Registration of SIM Cards) Regulation (the Registration Regulation) took effect on 1 September 2021 to implement the Real-name Registration Programme for SIM cards (Real-name Registration Programme).
OFCA assisted the CA in the formulation and issue of the “Guidelines on Implementation of Real-name Registration for SIM Cards” (the Registration Guidelines) on 20 August 2021 to provide practical and administrative guidance to licensees for implementation of the Real-name Registration Programme.
OFCA has been closely liaising with the licensees through the regular liaison meetings to ensure that their real-name registration systems are simple and easy to use and in compliance with the Registration Regulation. For five licensees which had failed to put in place in a timely manner an electronic registration system in accordance with the Registration Guidelines, the CA, having considered OFCA’s assessment and the licensees’ representations, issued directions to the five licensees on 8 March 2022 for rectification. Four out of the five licensees subsequently complied with the directions to the satisfaction of the CA. As for the remaining licensee which did not comply with CA’s direction, the CA issued a notice on 7 April 2022 to suspend its licence in respect of offering local mobile service through SIM cards for a period of 12 months with effect from 7 June 2022.
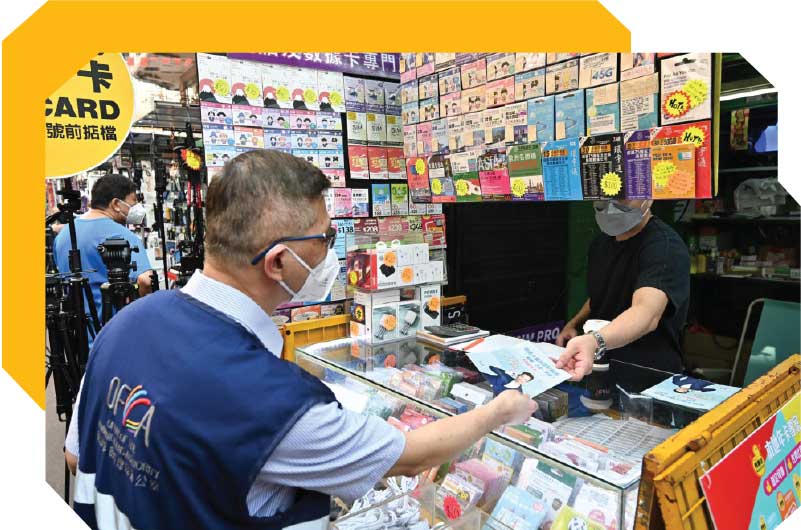

OFCA conducted market surveillance in Sham Shui Po District to ensure effective implementation of the Real-name Registration Programme for SIM Cards.
Apart from the above enforcement work, OFCA has also undertaken other on-going follow-up actions to ensure the effective implementation of the Real-name Registration Programme, such as registration testing of licensees’ electronic registration platforms, surveillance inspections in the market and inspections of the registration records.
OFCA has set up a thematic website (https://www.ofca.gov.hk/simreg) and hotline (2961 6699) to enhance public awareness of the Real-name Registration Programme. In addition, OFCA also supported CEDB in rolling out a host of publicity materials such as APIs, posters, leaflets, etc. to appeal to the public for early registration of their SIM cards. To cater for the needy groups in particular the elderly, OFCA has also assisted in setting up service counters at 18 designated post offices for helping members of the public to complete registration and conducted briefings to relevant non-governmental organisations.
OFCA will closely monitor the registration situation and step up publicity and support measures where necessary so as to ensure that users can complete real-name registration for their SIM cards in accordance with the Registration Regulation and before the statutory deadline of 23 February 2023.
The Class Licence for Offer of Telecommunications Services (CLOTS) regulates persons who offer telecommunications services to the general public without the establishment of any means of telecommunications. Under the previous version of the “Guidelines for Administration of CLOTS” (CLOTS Guidelines), only CLOTS licensees with a customer base of 10 000 subscriptions or more were required to register with the CA. To tie in with the implementation of the Real-name Registration Programme, OFCA assisted the CA to update the CLOTS Guidelines to require all CLOTS licensees intending to offer SIM services during the course of business, irrespective of the size of their customer base, to register their information with the CA before commencing the offer of SIM services. To facilitate CLOTS licensees to register with the CA under the enhanced requirements, an automated electronic platform was launched to allow the licensees to submit and update their business information online. As of 31 March 2022, 56 CLOTS licensees had been registered. OFCA will continue to assist the CA to ensure smooth operation of the enhanced registration system for CLOTS.
With the advent of technology, there are emerging new Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) devices operating in the 5925 – 6425 MHz band (such as the commonly known Wi-Fi 6E devices and collectively referred to as “6 GHz devices”) which support better performance in terms of faster data rates and lower latency. To enable the introduction of 6 GHz devices into Hong Kong, OFCA assisted the CA to conduct a public consultation during November and December 2021 to solicit views of the industry and interested parties on the creation of a class licence for regulating the use of and trade in 6 GHz devices for WLAN and variation to the existing class licence for provision of public WLAN services to allow the use of 6 GHz devices for provision of public WLAN services. Taking into account the feedback received in response to the public consultation, the decisions on the creation and variation of class licences for 6 GHz devices were promulgated by the CA in April 2022.

OFCA received an application from Hutchison Telephone Company Limited (Hutchison) seeking the CA’s approval to cease its provision of 2G services in September 2021. Under the relevant licence condition, MNOs are required to make proper and appropriate arrangements for the affected customers to the satisfaction of the CA before ceasing to provide a generation of mobile service. OFCA assisted the CA in vetting Hutchison’s application. The CA granted consent in July 2021 to Hutchison to cease the provision of all its 2G services starting from 30 September 2021, having taken into account relevant considerations including the extremely low percentage of customers to be affected by the 2G service cessation; incentive offers provided by Hutchison to the affected customers to migrate to a higher generation of mobile services; favourable termination arrangements for those who chose not to continue the subscription; and sufficient time of notification and customer support to the affected customers. Hutchison ceased its 2G services as scheduled.
As part of the ongoing effort to maintain an effective regulatory regime conducive to the business operation of the telecommunications industry, OFCA has been supporting the CA to introduce streamlining measures to keep up with the advancement of telecommunications technologies and help enhance operational efficiency. During the year, OFCA assisted the CA to conduct a review of the accounting practices the relevant licensees are required to follow, with a view to streamlining the reporting requirements, thereby reducing the industry’s compliance cost. OFCA will further assist the CA to consult the industry before adopting the streamlined reporting requirements for implementation.
Public payphone service is a form of basic telephone service which the universal service provider (USP) is required to provide under its universal service obligation (USO). The cost of providing a public payphone service subject to the USO is shared by the fixed and mobile services operators. In view of the diminishing demand for public payphone service in recent years, OFCA supported the CA to conduct a review of the reasonable number of public payphones that should be subject to the USO from 2017 to 2019.
For in-building type public payphones, the CA decided to exclude 515 in-building type public payphones (about 35% of the total number of in-building type public payphones) from the USO. All the excluded in-building type public payphones have been removed by the USP. For kiosk type public payphones, the CA decided to exclude 765 kiosk type public payphones (about 50% of the total number of kiosk type public payphones) from the USO. As of March 2022, over 96% of the excluded kiosk type public payphones had been dismantled.
With the continuous network rollout of FNOs, the Hong Kong community can enjoy nearly ubiquitous coverage of broadband networks deploying various technologies. As of March 2022, there were around 2.9 million residential and commercial fixed-broadband subscriptions, with a household penetration rate of 98%. Broadband services are now available at speeds of up to 10 Gbps. Around 86% of the fixed broadband subscriptions are supported by broadband services with speeds of 100 Mbps or above.
According to a report issued by the Fibre to the Home Council Europe in May 2022, Hong Kong was ranked fifth worldwide in fibre to home/building household penetration among the 84 economies under comparison.
With the support of OFCA’s single-point-of-contact service, a new submarine cable system, Hainan to Hong Kong Express (H2HE), was put into service in September 2021, and several new regional or transcontinental submarine cable systems as well as four domestic systems are under construction and scheduled to be put into service between 2022 and 2024. OFCA will continue to assist operators in applying for the necessary statutory approvals for the construction and landing of new submarine cable systems in Hong Kong.

In order to reinforce Hong Kong’s role as a regional telecommunications hub and meet the growing demand for external telecommunications facilities in Hong Kong, OFCA has been working with the relevant bureaux and departments to make available suitable land lots in the Chung Hom Kok Teleport for external telecommunications infrastructure, so as to further enhance the overall capacity and diversity of Hong Kong’s external telecommunications networks. Following a tender exercise conducted by the Lands Department, a land lot at Chung Hom Kok Teleport was granted to the successful tenderer in April 2022. Tender for disposal of another land lot at Chung Hom Kok Teleport was conducted between June and July 2022.
The land leases of 42 sites granted to telecommunications operators for establishing and operating telephone exchanges and other telecommunications-related facilities will expire in 2025. To facilitate the Government’s consideration of the way forward for handling these sites upon lease expiry, OFCA commissioned a consultancy study to review the current use of these sites and conducted a technical assessment of these sites based on the outcome of the consultancy study. OFCA will continue to provide support and advice to the Government on the matter from the telecommunications perspective.
OFCA assisted the CA to conduct a consultancy study on non-ionising radiation (NIR) safety of RBSs, including 5G RBSs. The study examined technical matters in relation to NIR, in particular those for 5G RBSs employing new technology like massive multiple-input-multiple-output antennas, reviewed the methodology for assessment of NIR for different RBS deployment scenarios and the existing regulatory measures, and made recommendations on practical measures to control the radiation safety of RBSs so as to facilitate the on-going development of public mobile services. The study was commenced in April 2021 and completed in June 2022.
Satellite spectrum and orbital positions are scarce natural resources. The use of these resources by communications satellites registered in Hong Kong should comply with the coordination and notification requirements of the International Telecommunication Union. In this regard, OFCA supports the licensed satellite operators of Hong Kong to coordinate with foreign administrations from time to time, and assists in the processing of licences for the operation of satellites in space orbits. There are now nine satellites in orbit operated by two Hong Kong companies licensed to provide satellite communications services.

OFCA closely monitors international developments in telecommunications standardisation and updates local technical standards in order to meet the needs of the industry and the public. In 2021/22, six revised technical standards covering single-standard and multi-standards 5G base stations and user equipment supporting 5G standalone and non-standalone operation were approved and issued by the CA.
Qualified local and overseas testing laboratories are now providing testing and certification services for various kinds of telecommunications equipment against technical standards prescribed by the CA. In particular, local laboratories accredited by the CA as local certification bodies (LCBs) offer a full range of telecommunications equipment testing and certification services. In 2021/22, LCBs and foreign certification bodies issued 527 equipment certificates to meet the needs of the telecommunications equipment market.
To ensure that all LCBs providing telecommunications equipment testing and certification services meet the service quality and performance standards required by OFCA, OFCA will continue to closely monitor their performance by regularly conducting documentary checks, plant visits and reviews. So far, all LCBs have been performing up to the requirements set by OFCA.